Comparative genomics of Pedicoccus pentosaceus isolated from different
niches reveals genetic diversity in carbohydrate metabolism and immune
system
Journal & Pages: Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11:253
Abstract: Pediococcus pentosaceus isolated from fermented food and the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and animals have been widely identified, and some strains have been reported to reduce inflammation, encephalopathy, obesity and fatty liver in animals. In this study, the genomes of 65 P. pentosaceus strains isolated from human and animal feces and different fermented food were sequenced and comparative genomics analysis was performed on all strains along with nine sequenced representative strains to preliminarily reveal the lifestyle of P. pentosaceus, and investigate the genomic diversity within this species. The results reveal that P. pentosaceus is not host-specific, and shares core genes encoding proteins related to translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis and signal transduction mechanisms, while its genetic diversity relates mainly to carbohydrate metabolism, and horizontally transferred DNA, especially prophages and bacteriocins encoded on plasmids. Additionally, this is the first report of a type IIA CRISPR/Cas system in P. pentosaceus. This work provides expanded resources of P. pentosaceus genomes, and offers a framework for understanding the biotechnological potential of this species.
Figures:
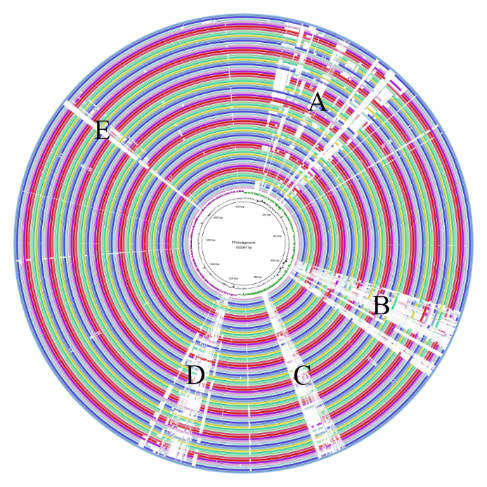
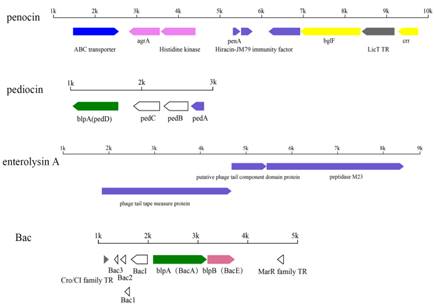
【作者提要】
戊糖片球菌作为片球菌素的天然生产者已被广泛应用于食品业、发酵业、渔业等。随着对戊糖片球菌的了解日益加深,研究人员发现其本身有着很大的益生潜力,比如能够调节炎症因子,降低胆固醇等。本研究从基因角度出发,运用比较基因组分析方法,对戊糖片球菌进行功能基因和比较基因组的分析,从而加深对其基础功能以及菌株间差异的了解,从基因层面推测其潜在的益生功能,为未来进一步的功能挖掘奠定基础。
Authors &Affliations:
Jie Jiang 1,2, Bo Yang1,2,4,*, R. Paul Ross4,5, Catherine Stanton4, 6, Jianxin Zhao1,2,3, Hao Zhang1,2, 3, 8, and Wei Chen1,2, 3, 7
1 State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
2 School of Food Science and Technology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
3 National Engineering Research Center for Functional Food, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
4 International Joint Research Center for Probiotics & Gut Health, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China
5 APC Microbiome Ireland, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland
6 Teagasc Food Research Centre, Moorepark, Fermoy, Cork, Ireland
7 Beijing Innovation Center of Food Nutrition and Human Health, Beijing Technology and Business University (BTBU), Beijing, China
8 Wuxi Translational Medicine Research Center and Jiangsu Translational Medicine Research Institute Wuxi Branch
Link:https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00253
 current location:
ICPG
>
Publications
>
Content
current location:
ICPG
>
Publications
>
Content