Increased cadmium excretion due to oral administration of Lactobacillus
plantarum strains by regulating enterohepatic circulation in mice
Journal & Pages:Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019,67(14): 3956-3965.
Abstract: The heavy metal cadmium (Cd) is a contaminant widely distributed in the food-chain. In the present study, eight-week oral administration of a probiotic strain, Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8610, markedly decreased blood Cd levels in volunteers. Further animal study showed that three L. plantarum strains administered orally exhibited significantly different effects on the regulation of bile acid (BA) metabolism and Cd excretion in mice. Among the strains, L. plantarum CCFM8610 showed the most significant effects on enhancing hepatic BA synthesis, biliary glutathione output, and fecal BA excretion. Biliary Cd output and fecal Cd excretion were markedly increased after L. plantarum CCFM8610 administration, resulting in a marked reduction in tissue Cd levels. The regulation of BA homeostasis and Cd excretion was due to the suppression of the enterohepatic farnesoid X receptor-fibroblast growth factor 15 (FXR-FGF15) axis by L. plantarum CCFM8610 and could be abolished by treatment with the FXR agonist GW4064. The regulatory effects were also related to the gut microbiota, as antibiotic pre-treatment reversed L. plantarum CCFM8610-induced effects in BA and Cd metabolism.
Figures:
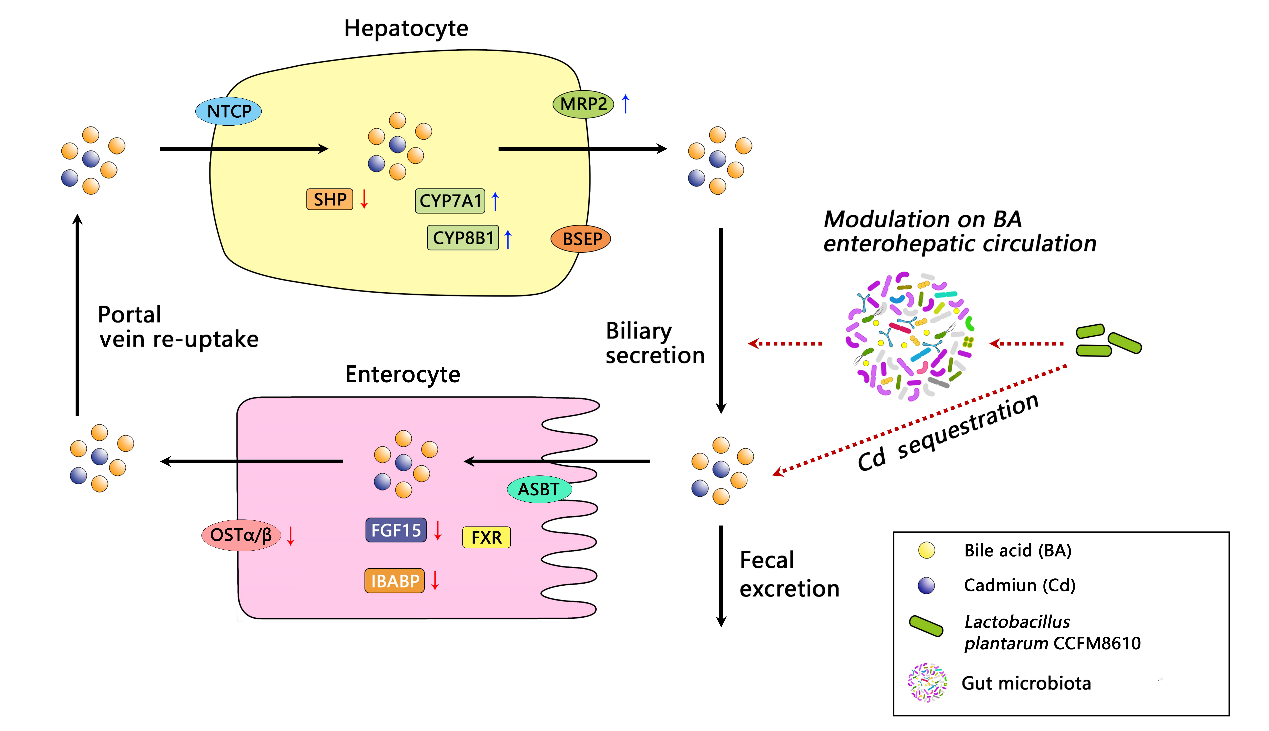
【作者提要】
解析了植物乳杆菌CCFM8610通过调节宿主胆汁酸干肠循环而影响重金属镉代谢的机制。证明菌株可以影响FXR-FGF15相关信号通路,促进胆汁酸的分泌和排出,从而加速镉的排出,相关调控机制依赖于肠道菌群。
Authors:
Zhai, QX [ 1,2 ] ; Liu, Y [ 1,2 ] ; Wang, C [ 1,2 ] ; Zhao, JX [ 1,2 ] ; Zhang, H [ 1,2,3 ] ; Tian, FW [ 1,2 ] ; Lee, YK [ 4 ] ; Chen, W [ 1,2,3,5 ]
[ 1 ] Jiangnan Univ, State Key Lab Food Sci & Technol, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Jiangnan Univ, Sch Food Sci & Technol, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 3 ] Natl Engn Res Ctr Funct Food, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 4 ] Natl Univ Singapore, Dept Microbiol & Immunol, Singapore 117597, Singapore
[ 5 ] Beijing Technol & Business Univ, Beijing Innovat Ctr Food Nutr & Human Hlth, Beijing 100048, Peoples R China
DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01004
Published:2019-4-10
 current location:
ICPG
>
Publications
>
Content
current location:
ICPG
>
Publications
>
Content